Axonal Guillain Barre Syndrome
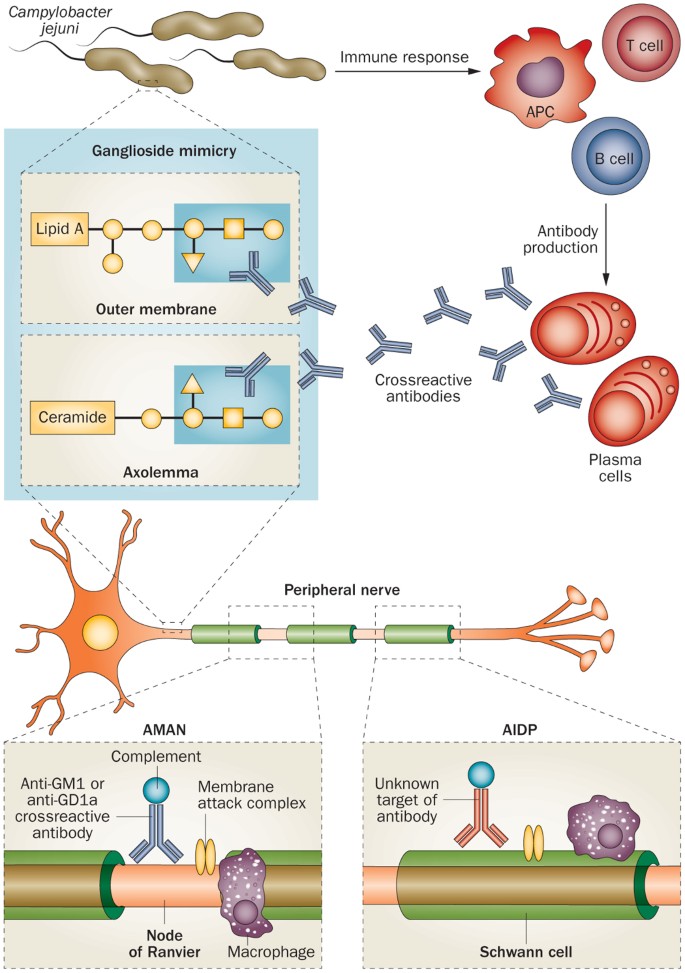
Axonal guillain barre syndrome. Electrodiagnostic criteria showed acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in 36 of the patients and acute motor axonal neuropathy AMAN in 38. Hughes RAtkinson PCoates PHall SLeibowitz S Sural nerve biopsies in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Acute motor axonal neuropathy AMAN an axonal subtype of Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is characterized by pure motor involvement frequent antecedent infection by Campylobacter jejuni association with anti-GM1 or anti-GD1a immunoglobulin G IgG antibodies and the electrophysiological features of axonal degeneration and reversible conduction block.
The first symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome involve motor and sensory control as the condition damages motor neurons. On average the rate of progression ranges from one day to over four weeks depending on the severity. 199215568- 577Google Scholar Crossref.
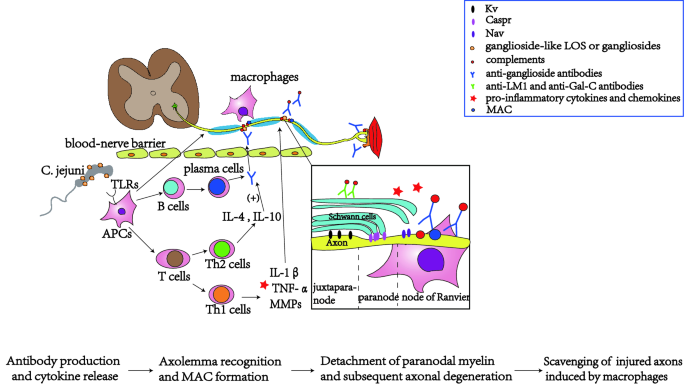
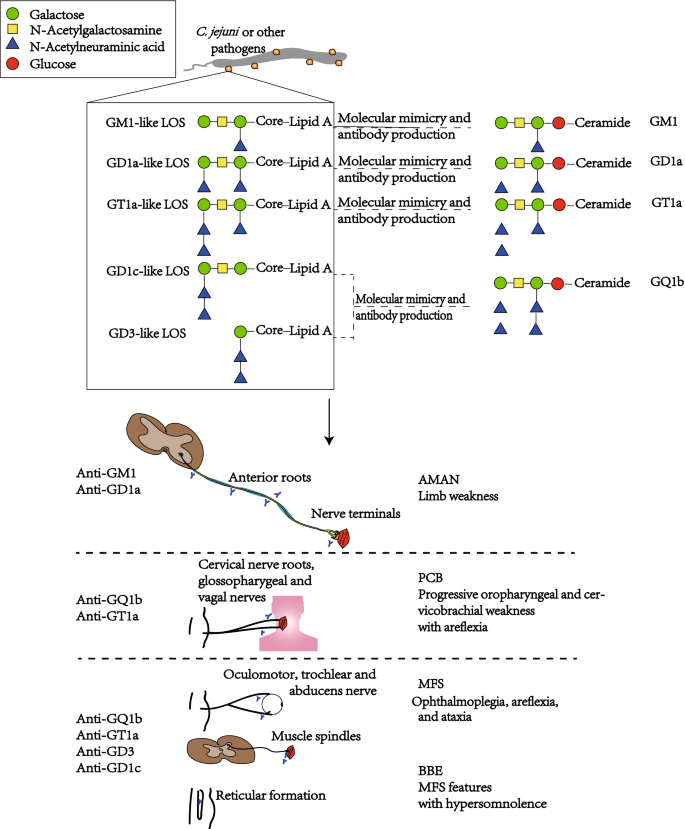
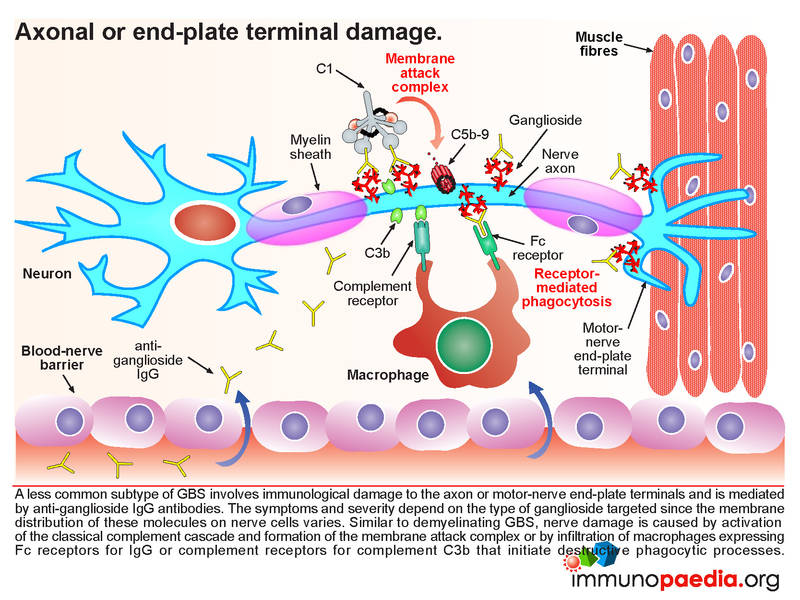
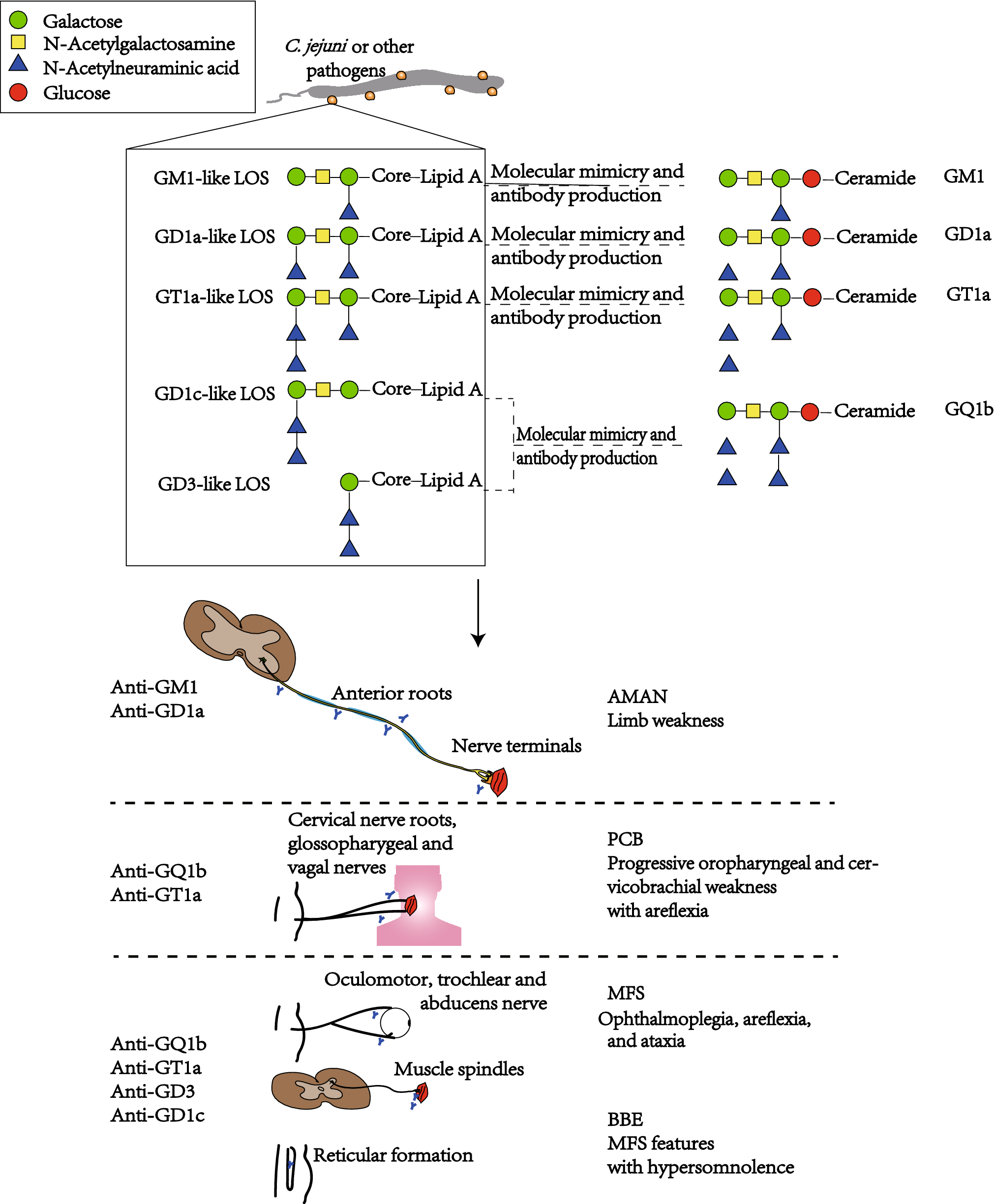
On the basis of pathological and electrophysiological observations GuillainBarré syndrome GBS has been regarded as a type of demyelinating neuropathy. Molecular mimicry of human gangliosides by a pathogens lipooligosaccharides is a well-established mechanism for Campylobacter jejuni -associated GBS. In Asia and Central and South America it is the major subtype of GBS seen in 3065 of patients.
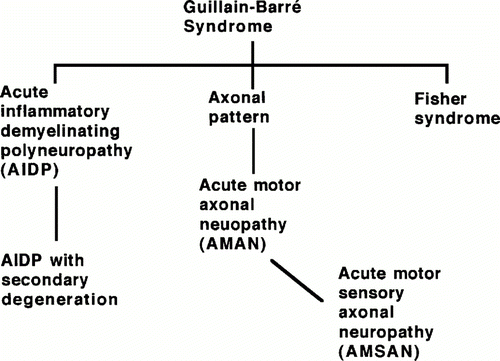
Guillain-Barre syndrome begins as weakness that progresses to full-body paralysis. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is a rare neurological disorder in which the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous systemthe network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord. Axonal variants of GuillainBarré syndrome GBS mainly include acute motor axonal neuropathy acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy and pharyngeal-cervical-brachial weakness.
Acute motor axonal neuropathy AMAN is a pure motor axonal subtype of Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS that was identified in the late 1990s. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is an acute-onset immune-mediated disease of the peripheral nervous system. Thomas Severe pulmonary hypertension associated with the acute motor sensory axonal neuropathy subtype of Guillain-Barré syndrome Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 101097PCC0b013e3181b0133d 11 1 e16-e19 2010.
Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS has been classified on a pathologic basis into demyelinating and axonal forms. It may be classified into 2 main subtypes. To clarify the relations of the axonal form of Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS to anti-ganglioside antibodies and Campylobacter jejuni infection 86 consecutive Japanese GBS patients were studied.
Prognosis in axonal GuillainBarré syndrome A primary axonal form of GuillainBarré syndrome was first described by Feasby and colleagues1 in 1986. AIDP patients frequently have a significantly long progression after the first examination.
Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is a rare neurological disorder in which the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous systemthe network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Initial indications were that this had a worse prognosis than demyelinating forms of the disease and it was suggested that recovery might require axonal regeneration along the entire length of the nerve fibre. Electrodiagnostic criteria showed acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in 36 of the patients and acute motor axonal neuropathy AMAN in 38. Demyelinating AIDP and axonal AMAN. It may be classified into 2 main subtypes. 199215568- 577Google Scholar Crossref. AIDP patients frequently have a significantly long progression after the first examination. On average the rate of progression ranges from one day to over four weeks depending on the severity. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is an acute-onset immune-mediated disease of the peripheral nervous system. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS has been classified on a pathologic basis into demyelinating and axonal forms.
Demyelinating AIDP and axonal AMAN. Acute motor axonal neuropathy AMAN is a pure motor axonal subtype of Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS that was identified in the late 1990s. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS has been classified on a pathologic basis into demyelinating and axonal forms. On average the rate of progression ranges from one day to over four weeks depending on the severity. The first symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome involve motor and sensory control as the condition damages motor neurons. Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS is a rare neurological disorder in which the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous systemthe network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord. To clarify the relations of the axonal form of Guillain-Barré syndrome GBS to anti-ganglioside antibodies and Campylobacter jejuni infection 86 consecutive Japanese GBS patients were studied.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Axonal Guillain Barre Syndrome"